GTAW Welding

Introduction
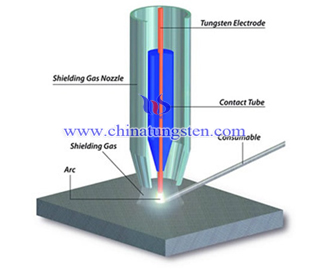
The full name of GTAW is Gas Tungsten Arc Welding, also call inert gas argon arc welding, namely TIG.
Material
GTAW welding material comprises a filler material and shielding gas. In a way, tungsten electrode is welding materials. When welding thin workpieces, it is no need to use a filler material, but most applications require the use of filler material. Diameter filler rod (wire) depends on the thickness of the base material. The thickness of the base material also determines the size of the welding current.
American Welding Society issued the technical requirements for GTAW welding filler material, the most widely used is the "carbon steel gas welding filler material technical requirements", the technical requirements applicable to GTAW, PAW, GMAW welding and other methods. Prefix R for GTAW filler rods, R means that filler rod is not a part of the welding circuit. Manual GTAW using a certain length filler rod, automatic GTAW welding using filler wire coil. Filler material technical requirements of AWS cover the most filler metal of weldable materials.
Electrode Selection
The electrode of GTAW TIG is tungsten electrode or tungsten alloy, because tungsten has the highest melting point of all metal, approximately 6170℉ (3410 ℃). Tungsten and tungsten alloy electrode technical requirements established by the American Welding Society includes eight standard tungsten. Tungsten has two supply states, chemical cleaning or polishing state. Chemical cleaning refers to the state that the tungsten has been drown or forged by chemically clean. Polishing means a kind of tungsten that has a uniform diameter and smooth surface after grinding. Tungsten surface of polished state is very smoothing with perfectly cylindrical, and therefore it can be more stably to delivery heat to tungsten clip. The range of tungsten diameter is 0.20 ~ 0.25in (0.5 ~ 6.4mm), length is 3 ~ 24in (76 ~ 610mm).
Notices
In GTAW welding, the size of tungsten electrode should match to tungsten, ensuring to clamp tungsten, so that the heat can be transmitted to the gun body. Extending the length of the tungsten f tungsten folder should be as short as possible.
Tungsten electrode holder and nozzle should be kept clean to ensure good protective gas flow. Diameter of the electrode must be selected in according with the type of current, the workpiece type and current. For welding a particular material, the required size can be found in the current welding parameters table (card). For example, AC GTAW, welding current is 100A, choosing 5 / 52in or 1 / 8in (3.2mm) of pure tungsten, if choose alloyed tungsten, then the users can choose 1 / 16in (1.6mm) or 3 / 52in. If the craft table requires DC positive polarity connection (DCEN) or DC reverse polarity connection (DCEP), users need the different tungsten diameter and exchanges. Welders may first select tungsten diameter based on experience. If choose pure tungsten for arc welding, the electrode tends to overheat and easily melt to tungsten surface. If this occurs, it means that welding current is too large for the selected diameter. If it has the melting phenomenon, it is likely to cause cross-contamination between tungsten and work piece. Users should use larger diameter pure tungsten or the same diameter. Too large or too small electrode diameter will cause excessive loss of tungsten.
If the current is too small or tungsten size is too big, it would cause arc drift. The tip shape can solve this problem, which can also help to improve the directivity of the arc. Select the appropriate size of the tungsten electrode can make it work as close to its maximum current-carrying. After extinction, the surface should have metallic luster, and tungsten electrode should not make contact with the molten pool during welding, or molten pool would be contaminated.